How planning works
Planning helps you to meet the demands which are created in various ways in Sage 200.
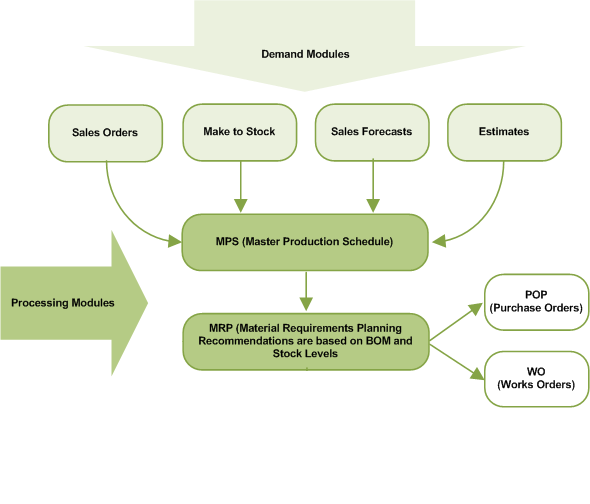
The first step in planning is to create the demands.
Demands can be created in the following ways.
- Entering sales orders Documents that state the quantity, description and price of goods and services ordered. They also specify agreed payment terms and discounts, delivery details and other agreements pertinent to the sale and its supply..
- Entering and releasing estimates Forecast project costs, based on expected costs of labour, machinery and operation times. In Manufacturing, estimates are produced for one-off items or non-repetitive batches., planned by stage.
- Entering and releasing sales forecasts The best estimate of future requirements. This is used as input to the MPS (Master Production Schedule). Forecast orders received should be subtracted from the forecast to leave a residual forecast in the master schedule. Total demands can then be calculated as orders plus residual forecast for each time period..
- Entering and releasing make to stock items, for which there are no specific demands.
Demands from these modules feed into the MPS module. The list of demands is then broken down through Materials Requirements Planning Materials Requirements Planning (MRP). MRP recommends purchase orders, transfers and work orders to balance supply and demand. in the MRP module. Recommendations are made to raise purchase orders or works orders, depending on stock levels.
Estimates, make to stock items and sales forecasts must be released in order to be included in the Master Production Schedule.
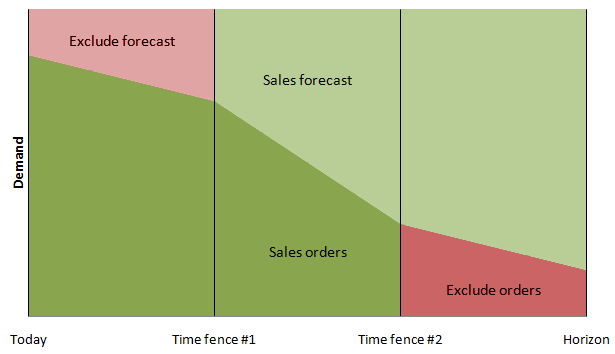
Time Fences, set on Planning settings MPS tab are used to set the points where the planning rules change that determine how MPS will read sales orders Documents that state the quantity, description and price of goods and services ordered. They also specify agreed payment terms and discounts, delivery details and other agreements pertinent to the sale and its supply. and sales forecasts The best estimate of future requirements. This is used as input to the MPS (Master Production Schedule). Forecast orders received should be subtracted from the forecast to leave a residual forecast in the master schedule. Total demands can then be calculated as orders plus residual forecast for each time period..
Time fences control the planning rules that determine how sales orders and sales forecasts are read by MPS.
The time fences are calculated from today's date, adding the number of days stored for Time Fence #1 and Time Fence #2.
Between today's date and the Time Fence #1 date (the emergency time fence), only the demand from sales orders are read by MPS. Any sales forecasts in this time period (based on their due date) are not read by MPS, as they cannot be fulfilled in time if they become orders.
In the period between Time Fence #1 and Time Fence #2, MPS will read the quantities of both sales orders and sales forecasts (using the higher value). The values will be netted off into buckets (if enabled).
The period after Time Fence #2 is for long term planning. After this date, only sales forecasts are read. Any sales orders are ignored by MPS because they are too far in the future.
Once demands are read, they are included in the Master Production Schedule or in a list of excluded demands. Demands may be excluded for various reasons.
- The sales order is on hold.
- The demand is beyond the horizon date A date beyond which data will not be included in the schedule. Data with a due date beyond the horizon date will not be read into the production schedule by MPS (Master Production Scheduling).. This defaults to today's date but you can change it when you read demand or set a default for it in the MPS tab of Planning Settings.
- The item does not have a due date.
- The sales order is a pro forma or quotation.
- The sales order has been cancelled.
- The Use only in BOM module option has been selected on the BOM Details tab.
- The sales order was created by Estimating.
- The item has not been released to production.
- The sales forecast falls in the Time Fence #1 number of days.
- The sales order due date falls outside the Time Fence #2 number of days.
- The sales order line is flagged for exclusion from MPS.
- Sales Order fulfilment method is set in the Stock Control Settings SOP Fulfilment Methods tab to Direct To Customer.
- The customer is on hold.
- A warehouse has not been specified.
- The sales order has been completed.
MPS facilitates back-to-back ordering (the generation of purchase orders to satisfy sales orders) for non-manufactured items.
Sales orders can be linked with batch works orders that are created specifically to meet the demands in the sales orders.
You can specify using the Flag Sales Order Line as Linked setting on the Manufacturing tab in Sales Order settings if you want the sales order to be linked with the works order that is created to satisfy the demand for the sales order. This link is then made when the sales order is created and saved. A batch works order is raised automatically for the sales order when the sales order is saved.
You can remove the link in Works Order processing.
If you don't use the Sales Order Processing method to link sales orders with works orders, you can still link sales orders to works orders in the MPS module in the following way.
-
In MPS, select the sales orders that you want to link and choose Link Sales Orders.
Note: The Linked column in the MPS - List is set to Yes.
-
In MRP, run MRP to make a recommendation to raise a works order to fulfil the sales order.
The Linked To column in the MPS - List displays the MRP Recommendation reference number.
If you set links up in MPS you can remove them by unlinking the sales orders also in MPS.
Note: You cannot remove links in MPS that have been set in Sales Order Processing. To remove those links you must unlink the works orders, using the Unlink Works Order option.
When you have a Master Production Schedule Master Production Schedule (MPS). The planning of production (usually end item production), to satisfy current and forecast sales orders. The sum of MPS items must equal the agreed sales and operations plan for the items over each planning period. Planning periods are normally a month or a four week period. Items planned within MPS are exploded by MRP (Materials Requirements Planning) to produce the material and capacity requirements., you can run MRP to produce the material requirements schedule. For most items, this considers stock levels and looks at items where stock is below the reorder point. The list of demands is exploded through BOM A stock assembly and process costing system, which provides facilities to specify the structure of finished items in terms of sub-assemblies and components. structures, taking into account the current and projected stock levels. From this, a series of recommendations is generated. Recommendations may be to make other items (raise a works order The authority to produce a part using the components specified on a BOM and the process specified on the routing.) or buy them (raise a purchase order).
Note: Buy recommendations are not made if the POP order generation option in POP settings Order Generation tab is set to Use Generate Orders. In this case MRP Materials Requirements Planning (MRP). MRP recommends purchase orders, transfers and work orders to balance supply and demand. will also not suggest any existing purchase orders are cancelled. We recommend you select either Use MRP or Use Both for the POP order generation option, if you are using MRP.
Items can be linked so that a purchase order meets the demands for a specific works order. If so, the demands for the specific works order are not included with the demands for other items.
Items can also be linked so that a raised batch works order fulfils the demands from a specific sales order. This can be set up in Sales Order Processing. It can also be set up in MPS. If it is set up in MPS Master Production Schedule (MPS). The planning of production (usually end item production), to satisfy current and forecast sales orders. The sum of MPS items must equal the agreed sales and operations plan for the items over each planning period. Planning periods are normally a month or a four week period. Items planned within MPS are exploded by MRP (Materials Requirements Planning) to produce the material and capacity requirements. then when MRP is run, the sales order is linked to the MRP Recommendation number for raising the works order.
Note: You cannot create purchase orders for back-to-back sales orders, when you create purchase orders from MRP recommendations.
You can modify recommendations in MRP.
Actioning recommendations raised in MRP creates a number of purchase and works orders.
You can action individual recommendations, a range of recommendations (by product, supplier, date, product family), or all recommendations.
Purchase recommendations are consolidated by supplier automatically. If you select multiple recommendations with the same supplier, and click Action, they are combined in one purchase order. If the due dates are the same, the recommendations are combined in one line on the order. If the due dates are different, multiple order lines are created.
SOP fulfilment methods (stock settings)
Set up link in SOP between sales and works orders
Removing a link set in SOP between sales and works orders
Link sales orders to works orders using MPS instead of using SOP to link them
Removing links set in MPS between sales and works orders
The Sage 200 Manufacturing module is now retired, from the Sage 200 Professional 2025 R2 release. We've retained the product help here for customers still using Manufacturing with older versions of Sage 200.
As the module is now retired there is no support from Sage. You can find out more about support in our product lifecycle (opens in a new tab). Please speak to your Sage Business Partner to find out more.