Reverse charge VAT to prevent carousel fraud (UK)
Reverse charge VAT is a term that covers the following scenarios:
-
Accounting for VAT as a reverse charge on services supplied to a UK business from abroad.
-
Accounting for VAT as a reverse charge on goods or services supplied to an Irish or Northern Irish business from an EU business.
- Accounting for VAT as a domestic reverse charge to prevent fraud in trade between businesses within the UK centres. This is known as carousel fraud or missing trader intra community (MTIC) fraud.
You set up VAT rates differently for each of these scenarios.
The HMRC introduced rules to combat the abuse of VAT regulations known as carousel fraud or missing trader intra community (MTIC) fraud. See HMRC: Domestic reverse charge procedure (VAT Notice 735) (opens in a new tab).
The rules cover any business selling or buying specified ranges of electronic devices, such as mobile telephones and computer chips, when an invoice for a UK VAT registered customer exceeds £5000.
In the past, a credit note is created for the return of the goods on the same value as the invoice. This amount is paid even if the credit note is less than £5000.
Under the new rules, the seller does not charge the buyer any VAT. However the invoice must clearly show the items that attract the reverse charge and the amount applicable. The HMRC have indicated that the wording should follow certain styles. The reports and invoices in Sage 200 follow these guidelines.
The buyer must record items where reverse charges have been applied separately from items where normal VAT has been applied. This allows you to identify these reverse charges when you run your VAT Return.
The HMRC have indicated that the wording should follow certain styles. The reports and invoices in Sage 200 follow these guidelines. The buyer must record items where reverse charges have been applied separately from items where normal VAT has been applied. This allows you to identify these reverse charges when you run your VAT Return.
What do you need to do if you want to use reverse charge VAT?
-
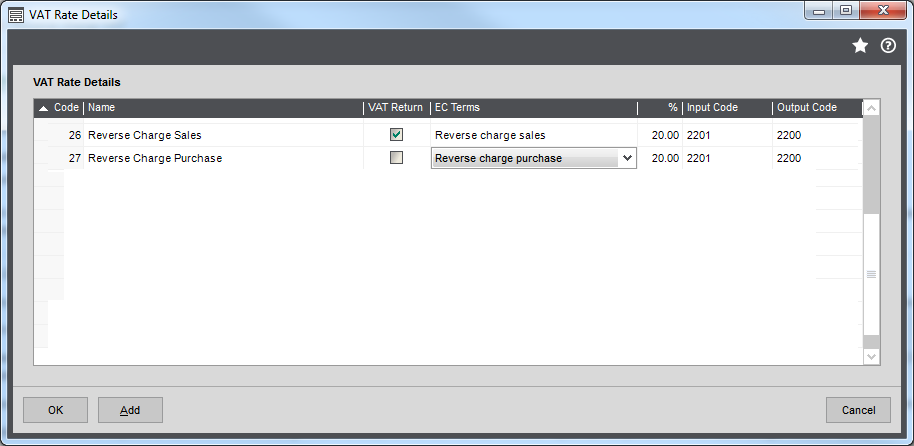
Set up the VAT rates.
Open: Settings > Organisational and Financial > VAT Rates.
-
If you are selling, set up the VAT Rate for Reverse charge sales (Mobiles).
- Select the VAT Return check box.
- Set the Terms to Reverse charge sales (Mobiles).
- Enter your local VAT rate for the reverse charge sales rate. This is normally 20%.
-
If you are buying, set up the VAT Rate for Reverse charge purchases (Mobiles).
- Set the Terms to Reverse charge purchases (Mobiles).
- Apply the VAT rate you have set up to appropriate acquisitions from EC supplies (outside the UK). This is normally 20%.
-
-
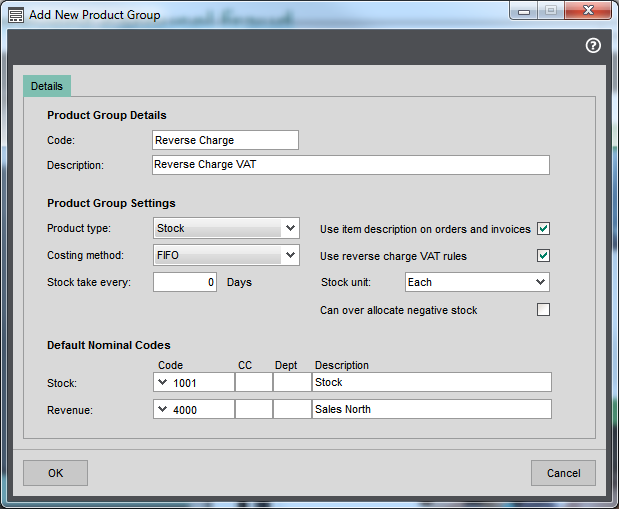
Ensure the appropriate product groups in Stock Control have reverse charge processing enabled.
Open: Settings > Stock Control > Product Groups.
- Edit the product group, then select Use reverse charge VAT rules on the Details tab.
-
Ensure that all goods that fall under the reverse charge VAT rules are linked to such a product group and have the correct settings selected.
Tip: You can override the product group setting Use reverse charge VAT rules on the stock item Analysis tab.
-
Specify that you want to apply reverse charge processing rules when printing invoices.
Open: Settings > Invoicing and Sales Orders > Invoice and Order Settings | Invoice Printing.
- Go the Invoice Printing tab.
- Select Apply domestic reverse charge VAT rules when printing invoice.
- Select the text you want to use on invoices and credit notes when the reverse charge is applied.
Produce the Reverse Charge Sales List (RCSL)
From July 2022, you are no longer to submit your Reverse Charge Sales List to HMRC.
However, you can still produce the Reverse Charge Sales List reports or CSV file for your own use.
-
Use the reports to view transactions that will appear on the RCSL.
Open: Customers > Customer Reports > Account Analysis > RCSL Report (Detailed) / (Summary)
-
Produce a CSV file with totals of the reverse charge sales in each period.
Open: Customers > Customer Reports > Account Analysis > Produce RCSL Declaration
Sage is providing this article for organisations to use for general guidance. Sage works hard to ensure the information is correct at the time of publication and strives to keep all supplied information up-to-date and accurate, but makes no representations or warranties of any kind—express or implied—about the ongoing accuracy, reliability, suitability, or completeness of the information provided.
The information contained within this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional advice. Sage assumes no responsibility for any action taken on the basis of the article. Any reliance you place on the information contained within the article is at your own risk. In using the article, you agree that Sage is not liable for any loss or damage whatsoever, including without limitation, any direct, indirect, consequential or incidental loss or damage, arising out of, or in connection with, the use of this information.
External websites